Skewness describes how the data points spread around the mean, particularly whether they lean more towards one side (left or right) or are relatively symmetrical
Types of Skewness:
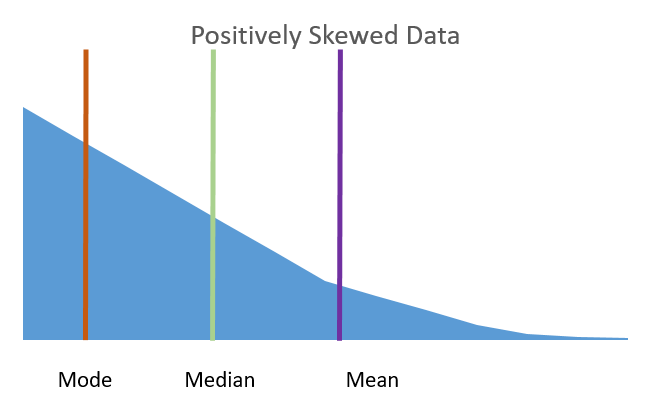
Positive Skewness: The tail of the distribution extends to the right. Larger number of data points above the mean
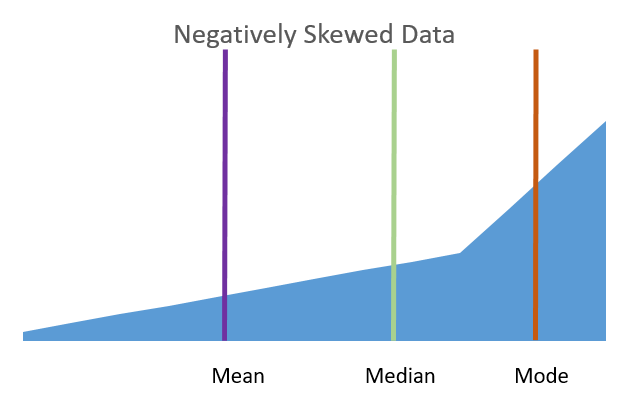
Negative Skewness: The tail of the distribution extends to the left. Larger number of data points below the mean
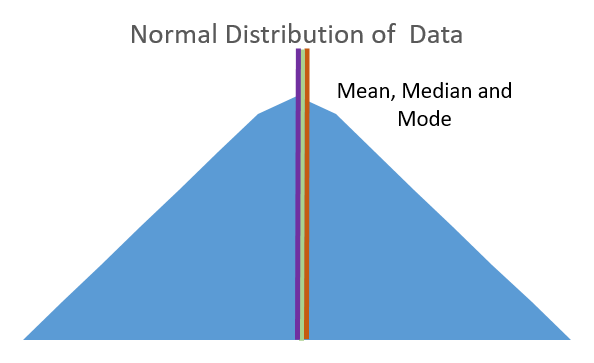
Zero Skewness: The distribution is symmetrical, with an equal tail on both sides